We are done visiting the mine, bullshit
Lunes, Agosto 28, 2017
Linggo, Agosto 27, 2017
Sabado, Agosto 26, 2017
UFC VS BOXING
It's bullshit.
Law of gravity beats Law of attraction
Illusion vs reality
Conor vs Floyd
Courage vs Money
That was just a big bitch slap.
Get back to reality, up, there goes gravity, up there goes gravity.
There's always a limit to all B.S.
Better learn physics than philosophy.
Better defend than attack, exploit the enemy, confuse the enemy, when strong, appear weak, when near appear far. This is the art of war --- to legally acquire wealth through drama, through toying with the stupidity of human desires and emotions. A perfect play would be taking the grand loot with the least effort.
The Art of War. Sun Tzu.
48 Laws of Power. Robert Greene.
All sports are nothing but a money making machine. Forget athleticism, forget manliness, everything is business.
There should be pawns to be played, there should be the piece to be used.
Straight Line Persuasion. Jordan Belfort.
Be the master deceiver.
Genghis Khan.
Floyd Mayweather Jr.
Be the professional con artist.
The Pink Panther.
The Joker.
Satan wins. every. single. time. :)
Never Drink Yakult at Night
It's 4 o'clock am and I'm shittin'.
These are what I swallow in reverse order last night:
Yakult 1 full drink>a few sips of Milk>a quarter of chocolate drink>tahong>rice>fried potatoes>banana>cookies>bread>>>>>>
Biyernes, Agosto 25, 2017
Grandma Linda and the Energy Meridians
Last summer break, I spent my time at grandma's house. In the morning we do garden work and in the evening I took care of the store.
For about three weeks there I noticed she wakes up early dawn precisely at five o'clock, I call the five o'clock crunch. It's interesting that she aligned her body to the natural cycle of the sun, all without the aid of alarm clock.
So I get up take water from the tap to boil it, after a while we will enjoy a warm cup of coffee or choco with crackers or bread. After that, we will feed the geese with boiled chayote fruit added with feeds which are dried yellow sweet corn.
There will be something to be done in this time like picking chayote fruit to be cooked in the evening or maybe carrying a sack of manure, or sharpening the knives, cleaning the house. All these are done about seven o'clock. A two hour perfect timing from the Energy Meridian.
We will cook rice, then the viand. Get the tools, pack the lunch, lock the house, go to work, walk in boots. Work mine o'clock to eleven o'clock but that's not the case. Work for an hour then snack, work again. Lunch would be twelve thirty pm.
We continue work on around two then finish around three thirty. There goes another day.
I always reflect on those moments when the sun is too hot and the weeds are too tough, why am I doing this? Then I reflect on food, I took the convenience of food for granted big time, at grandma's place, all food that pass through my lips are grown within the vicinity. Except for rice, meat, processed etc.
My luxury there was that candies that was sold in the store.
Happiness really is comparison.
Memories of the past will either make me curse or sing for gratitude. Should I then let myself fall to the deepest hole? Voluntarily, that is stupid, stepping on shit to learn it's not a good thing to do.
But why do this? If anything else, for experience.
When I was practicing programming in python I will not get satisfied until I write that code then test it, even how basic it was and repeating it sound stupid because I spend time doing things that wasn't just as important or of any use, but as 50 Cent say it, reality is a drug, the more I take it, the I thirst for more.
Going back, I think my grandma's way of life is beautiful and simple, I don't even know how to properly build a fire for heaven's sake, that experience humbled me, I never know until the hands do the talking.
Would I want such a life? A life in alignment with nature? Hell yeah! It requires hands-on on every movement of the day, that would be great to balance my day dreaming state, always in the "brown eye" the dreamer's gaze, because I learned that when you deliberately ignore reality, boy I should be prepared for a rude awakening.
Math is a great grounding, it's intellectually stimulating at the same time, making me think in reason, not in knee-jerk reaction.
So much for that, anyhow what I want to master was the art of fluidity of the mind, changing accordingly to the present, freely and effortlessly.
Miyerkules, Agosto 23, 2017
Physical Geology 10 | Chapter 3
http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/007252815x/student_view0/index.html
http://highered.mheducation.com/novella/SITELIBDisplay.jsp?mode=SEM&catId=903
1 A surface separating different types of rocks is called:
A) a chill zone.
B) a xenolith.
This is the correct answer.
C) a contact.
D) none of the above
2 The major difference between intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks is:
A) the type of minerals they contain.
This is the correct answer.
B) where they solidify.
C) their chemical composition.
D) all of the above
3 Which is not an intrusive rock type?
This is the correct answer.
A) andesite
B) granite
C) diorite
D) gabbro
4 By definition, stocks differ from batholiths in:
A) elevation above sea-level.
B) chemical composition.
C) shape.
This is the correct answer.
D) size.
5 On average, the geothermal gradient is about:
A) 50 degrees Celsius per kilometer.
This is the correct answer.
B) 30 degrees Celsius per kilometer.
C) 10 degrees Celsius per kilometer.
D) 1 degree Celsius per kilometer.
6 Which of the following minerals is part of Bowen's Continuous Series?
This is the correct answer.
A) plagioclase.
B) amphibole.
C) biotite.
D) pyroxene.
7 Which of the following minerals is part of Bowen's Discontinuous Series?
A) olivine
B) biotite
C) pyroxene
This is the correct answer.
D) All of these are part of Bowen's Discontinuous Series.
8 The difference in texture between plutonic and volcanic rocks is caused by:
A) different chemical compositions.
B) different amounts of water in the magma.
This is the correct answer.
C) different rates of cooling and crystallization.
D) different mineralogy.
9 A change in magma composition due to melting of surrounding country rock is called:
A) differentiation.
B) crystal settling.
This is the correct answer.
C) assimilation.
D) magma mixing.
10 Andesite is most often associated with what type of plate boundary?
A) reversible plate boundaries
This is the correct answer.
B) convergent plate boundaries
C) transform plate boundaries
D) divergent plate boundaries
11 You discover a rock with minerals large enough to be seen containing amphibole, biotite, and plagioclase. This is:
A) hornblende.
B) granite.
C) gabbro.
This is the correct answer.
D) diorite.
12 Bowen’s Reaction Series illustrates relations between:
A) temperature, pressure, and viscosity.
B) viscosity, temperature, silica content, and volatile content.
This is the correct answer.
C) temperature, chemical composition, and mineral structure.
D) temperature, viscosity, and mineral composition.
13 The two important criteria used for igneous rock classification are:
This is the correct answer.
A) texture and mineral composition.
B) temperature and viscosity.
C) mineral composition and temperature.
D) texture and temperature.
14 Basalt and gabbro:
A) formed from magma with the same silica content.
B) formed from magma with the same temperature.
C) have the same minerals.
This is the correct answer.
D) all of these
15 A rock with mineral crystals too small to be seen and low temperature minerals is:
A) granite.
B) andesite.
This is the correct answer.
C) rhyolite.
D) gabbro.
16 Igneous rocks that form entirely beneath Earth's surface are said to be:
A) platonic.
This is the correct answer.
B) plutonic
C) extrusive.
D) volcanic.
17 Andesite was named for a rock type commonly found:
A) in Mayberry, North Carolina.
This is the correct answer.
B) in the Andes Mountains.
C) in Hawaii.
D) in the Rocky Mountains.
18 Igneous processes are those which relate to:
A) solidification of magma.
B) formation of magma.
C) melting of rocks.
This is the correct answer.
D) all of these
19 The geothermal gradient of the asthenosphere is:
A) always changing as a result of plate tectonics.
B) the reverse of the geothermal gradient in the lithosphere.
This is the correct answer.
C) about 1 degree per kilometer.
D) the same as the temperature structure of the lithosphere.
20 Volcanic rocks are also:
A) Explosive.
This is the correct answer.
B) Extrusive.
C) Plutonic.
D) Intrusive.
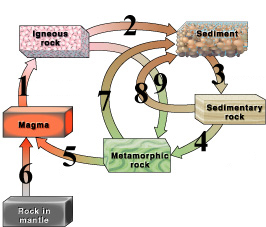


NOTE: CONTINUOUS VS DISCONTINUOUS
The continuous branch describes the evolution of the plagioclase feldspars as they evolve from being calcium-rich to more sodium-rich.
The discontinuous branch describes the formation of the mafic minerals olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite mica.
TERMS:
http://geology.com/minerals/plagioclase.shtml
maf·ic = relating to, denoting, or containing a group of dark-colored, mainly ferromagnesian minerals such as pyroxene and olivine
*PLUTONIC ROCKS are rocks beneath the Earth's crust which is a solidified magma while a volcanic rock is a solidified lava.
The name was taken from the God of the Underworld, Pluto or Hades
Sleep Magic
Sleep when it's about to clock in the dinner time which is 5-7 so sleep about 4:30, you are strong until midnight
..I will update next morning
Success! I don't feel mud
I will continue with the experiment
I don't know if I have rem sleep though
It's 7 so a 6 hour block of sleep
Engineering Economy | Introduction for Engineering Students
It is the analysis and evaluation of the
factors that will affect the economic
success of engineering projects to the
end that a recommendation can be
made which will insure the best use of
capital.
Source: Engineering Economy 3rd Edition
by Hipolito Sta. Maria
Basic Accounting Concepts
Introduction for
Engineering Students
Accounting
• It is a system for measuring, processing, and
communicating financial information. It is often referred
to as the language of business.
• It is generally a source of much of the financial data
needed in making estimates of future financial conditions.
• It is also a prime source of data for after-the-fact analyses
that might be made regarding how well an investment
project has turned out compared to the results that were
predicted in the engineering economy study.
• The process of identifying, measuring, and reporting
financial information of an entity.
ACCOUNTING
Is a system for measuring, processing, and
communicating financial information. It is
often referred to as the language of
business.
A key product of an accounting information
system, financial statements allow people
to make business decision.
Accounting’s Role in Business
Mission of the Business:
Provide a Product/Service
Functions directly
Relationship of Business with
related to the
mission:
- Production
- Purchasing
- Sales
- Service
- Human Resource (HR)
- Administration
- Accounting/ Financial Services
| Proprietorship | Partnership | Corporation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Owner(s) | Proprietor - One owner |
Partner - two or more owners |
Stockholders - generally many owners |
| 2. Life of entity | Limited by owner's choice or death | Limited by owner's choice or death | Indefinite |
| 3. Personal liability of owner(s) for business debts | Proprietor is personally liable | Partners are personally liable | Stockholders are NOT personally liable |
The Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
Economic Resources = Claims to Economic Resources
Assets = Economic Resources
Liabilities = (outsider claims) financial obligations to outsiders called creditors
Owner's Equity = (insider claims) claims held by the owner/s of the business
Accounting Equation Expounded
- An example of an asset would be your car. Your car has a dollar value attached to it. It adds value to your individual worth.
- An example of a liability would be your car loan. The loan removes value from your individual worth.
- The equity in your car would be any money you paid down toward the purchase.
- If you use your car to operate a pizza delivery service, the income generated from delivering pizzas would be known as revenue.
- Any expense for gas or car repairs would be recorded in an expense account known as “automotive expense”.
A = L + ( I - W + i - d )
A for assets
L for liabilities
I for investments
W for withdrawals
i for income
d for deductions from income or expenses
ASSETS
Classification of Assets
1. Current Assets
Improvements to International Accounting Standards
1(December 2003) classifies assets as current assets when it
is:
a) expected to be realized in, or s intended for sale or
consumption in, entity’s normal operating cycle;
b) held Primarily for the purpose of being traded;
c) expected to be realized within twelve months of the
balance sheet date; or
d) cash or a cash equivalent unless it is restricted from being
exchanged or used to settle a liability for at least twelve
expenses months after the balance sheet date.
Classification of Current Assets
• Cash includes coins, currencies, checks, bank deposits and other
cash items readily available for use in the operations of the
business.
• Cash Equivalent are short-term investments that are readily
convertible to known amounts of cash which are subject to an
insignificant risk to changes in value (per SFAS No. 22, revised
2000)
• Marketable securities are stocks and bonds purchased by the
enterprise and are to be held for only a short span of time or
short duration. They are usually purchased when a business has
excess cash.
• Trade and other Receivables includes the amounts collectible from any of the
following accounts:
Accounts Receivable — is the amount collectible from the customer to
whom sales have been made or services have been rendered on account or
credit.
Notes Receivable — is a promissory note issued by the client or the
customer in exchange for services or goods received as evidence of his/her
obligation to pay.
Interest Receivable — amount of interest collectible on promissory notes
received from costumers and clients.
Advances to employees - certain amount of money loaned to employees
payable in cash or through salary deductions.
Accrued Income — income already earned but not yet received.
• Inventories represent the unsold goods at the end of the accounting period.
This is applicable only to a merchandising business.
• Prepaid Expenses include supplies bought for use in the business or services
and benefits to be received by the business in the future paid in advance.
CONTRA-ASSET ACCOUNTS—these are accounts deducted from the related
asset accounts.
• Allowance for Bad Debts are losses due to uncollectible accounts, This is
deducted from the accounts receivable account to get the net reliable value. This
is in line with the financial statements qualitative characteristic of conservatism
wherein no profits would be anticipated but all probable or estimable losses
should be provided.
• Accumulated Depreciation represents the expired cost of property, plant and
equipment as a result of usage and passage of time, This is deducted from the
cost of the related asset account.
2. Non-Current Assets
Classification of Non-Current Assets
• Long-Term investment are assets held by an enterprise for the accretion of
wealth through capital distribution such as interest, royalties, dividends and
rentals for capital appreciation or for other benefits to the investing enterprise such as those
obtained through trading relationships. Investments are classified as long-term when
they are intended to be held for an extended period of time (International Accounting
Standard No. 25).
• Property, Plant, and Equipment are tangible assets that are held by an
enterprise for use in the production or supply of goods or services, or for
administrative purposes and which are expected to be used for more than one
period (International Accounting Standard No. 16).
Examples of Property, Plant, and Equipment
• Land is a piece of Lot or real estate owned by an enterprise on which a building can be
constructed for business purposes.
• Building is an edifice or structure used to accommodate the office, store, or factory of
business enterprise In the conduct of its operations.
• Equipment includes typewriter, air-conditioner, calculator, filing cabinet, computer, electric
fan, trucks, cars used by the business in its office, store, or factory, Specific account titles
may he used such as Office Equipment Store Equipment, Delivery Equipment
Transportation Equipment, Machinery, and Equipment.
• Furniture and Fixtures includes tables, chairs, carpets, curtains, lamp and lighting fixtures
and wall decors. Specific account titles may be used such as Office Furniture and Fixtures
and store Furniture and Fixtures.
• Intangible Assets are identifiable, non-monetary assets without physical substance held for
use in the production or supply of goods or services, or rental to others, or for
administrative purposes, These include goodwill, patents, copyrights, licenses, franchises,
trademarks, brand names, secret processes, subscription lists and non-competition
agreements (International Accounting Standards No. 38).
LIABI LITI ES
Improvements to International Accounting Standards 1 (December 2003)
classifies a liability as a current liability when it is:
a) Expected to be settled in the entity’s normal operating cycle;
b) Held primarily for the purpose of being traded;
c) Due to be settled within twelve months after the balance sheet date; or
the entity does not have an unconditional right to dofer settlement of
the liability for at least twelve months after the balance sheet date.
Classification of Current Liabilities
Trade and other payables - includes payables from any of the following
accounts:
Accounts Payable includes debts arising from purchase of an asset or
acquisition of services on account
Notes Payable includes debts arising from purchase of an asset or acquisition
of services on account evidenced by a promissory note.
Loan Payable is a liability to pay the bank or other financinginstitution arising
I rom funds borrowed by the business from these institutions payable within
twelve months or shorter. (Note: if the loan is payable within twelve months,
then it is classified under non-current liabilities,)
Utilities Payable is an obligation to pay utility companies for services received
from them. Examples of this are telephone services to PLDT, electricity to
Meralco and water services to Maynilad.
Unearned Revenues represent obligations of the business arising from
advance payments received before goods or services provided to the customer.
This will be settled when certain goods or services are delivered and rendered.
Accrued Liabilities include amounts owed to others for expenses already
incurred but not yet paid. Examples of these are salaries payables, utilities
payable, taxes payable, and interest payable.
Classification of Non-Current Liabilities
Non-Current Liabilities are no long term liabilities or obligations which are
payable for a period longer than one year. Examples of Non-current
Liabilities are as follows:
• Mortgage payable is a long-term debt of the business with security or
collateral in the form of real properties, In case the business fail to pay
the obligation, the creditor can foreclose or cause the mortgaged asset
to be sold and the proceeds of the sale to be used to settle the
obligation,
• Bonds Payable is a certificate of indebtedness under the seal of a
corporation, specifying the terms of repayment and the rate of interest
to be charged.
OWNER’S EQUITY
• Capital is an account bearing the name of the owner representing the original
and additional investment of the owner of the business increased by the amount
of net income earned during the year. It is decreased by the cash or other assets
withdrawn by the owner as well as the net loss incurred during the year.
• Drawing represents the withdrawals made by the owner of the business either
in cash nr other assets.
• Income Summary is a temporary account used at the end of the accounting
period to close income and expense accounts. The balance of this account shows
the net income or net loss for the period before it is closed to the capital account.
• Service lncome includes revenues earned or generated by the business in
performing services for a customer or client.
Examples: Laundry Services by a laundry shop
Medical Services by a doctor
Dental services by a dentist
• Salaries or wages Expense includes all payments made to employees or
workers for rendering services to the company. Examples are salaries or
wages, 13th month pay, cost of living allowances and other related benefits
related to them.
• UtilIties Expense is an expense related to the use of electricity, fuel, water,
and telecommunications facilities.
• Supplies Expense covers office supplies used by the business in the conduct
of its daily operations.
• Insurance Expense is the expired portion of premiums paid on insurance
coverage such as premiums paid for health or life insurance, motor vehicles
or other properties.
• Depreciation Expense is the annual portion of the cost of a tangible asset
such as buildings, machineries, and equipment charged as expense for the
year.
• Uncollectible Accounts Expense/Doubtful Accounts Expense/Bad Debts Expense
means the amount of receivables charged as expense for the period
because they are estimated to be doubtful of collection.
• Interest Expense is the amount of money charged to the borrower for the
use of borrowed funds.
TERMS DEFINED
Accounts Payable - money owed to creditors, vendors, etc.
Accounts Receivable - money owed to a business, i.e. credit sales
Accrual Accounting - a method in which income is recorded when it is earned and expenses are recorded when they are incurred
Asset - property with a cash value that is owned by a business or individual
Balance Sheet - summary of a company's financial status, including assets, liabilities, and equity
Bookkeeping - recording financial information
Chart of Accounts - a listing of a company's accounts and their corresponding numbers
Cost Accounting - a type of accounting that focuses on recording, defining, and reporting costs associated with specific operating functions
Credit - an account entry with a negative value for assets, and positive value for liabilities and equity.
Debit - an account entry with a positive value for assets, and negative value for liabilities and equity.
Depreciation - recognizing the decrease in the value of an asset due to age and use
Double-Entry Bookkeeping - system of accounting in which every transaction has a corresponding positive and negative entry (debits and credits)
Equity - money owed to the owner or owners of a company, also known as "owner's equity"
Financial Accounting - accounting focused on reporting an entity's activities to an external party; ie: shareholders
Financial Statement - a record containing the balance sheet and the income statement
Fixed Asset - long-term tangible property; building, land, computers, etc.
General Ledger - a record of all financial transactions within an entity
Income Statement - a summary of income and expenses
Job Costing - system of tracking costs associated with a job or project (labor, equipment, etc) and comparing with forecasted costs
Journal - a record where transactions are recorded, also known as an "account"
Liability - money owed to creditors, vendors, etc
Liquid Asset - cash or other property that can be easily converted to cash
Loan - money borrowed from a lender and usually repaid with interest
Net Income - money remaining after all expenses and taxes have been paid
Non-operating Income - income generated from non-recurring transactions; ie: sale of an old building
Note - a written agreement to repay borrowed money; sometimes used in place of "loan"
Operating Income - income generated from regular business operations
Payroll - a list of employees and their wages
Profit - see "net income"
Profit/Loss Statement - see "income statement"
Revenue - total income before expenses.
Single-Entry Bookkeeping - system of accounting in which transactions are entered into one account
Debits and Credits
Every single transaction recorded in the accounting process falls into one of two categories: it is either a debit or a credit.
A debit is a transaction of value “added” to an account.
A credit is a transaction of value “removed” from an account.
Debit, value is added.
Credit, value is removed.
For example, in your checking account, a deposit is a debit, a check is a credit.
How you apply those transactions, depends upon the type of account you are working with.
Accounts
Accounts are simply established to provide a record of individual business transactions as they apply to a certain area or item.
Your personal checking account is established in order to provide a record of individual personal financial transactions you create when you write a check.
All of the accounts are listed in a general ledger.
Today, the actual ledger book has long since been replaced by accounting software that creates a general ledger on the computer. The concept however has not been altered. The general ledger is the central location for maintaining all your accounts.
Journal entries refer to the posting or entering of the financial transactions to a particular account.
ACCOUNTING FOR BUSINESS TRANSACTIONS
TRANSACTION: is any event that affect the
financial positions of the business entity.
A transaction always has a value received and
value parted with.
— Value- property, cash, service, or a right.
• Transactions affect a business’s assets,
liabilities, and owner’s equity. Therefore every
transaction affects the accounting equation.
Accounting for Business Transaction
Transaction- is any event [liai affect the financial positions of the
business entity.
- a transaction always has a value received and value parted with
Value property, cash, service, or a right.
Is I Mr Lee bought land for the business
Value received- land
Value parted with—cash
Ex2 Mr. Lee paid the salary of helper.
Value received —services
Value parted with- cash
Es3: Mr Lee sold goods on account.
Value received — right to collect from customer
Velue parted with is goods
Transactions affect a business’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s
equity.
Therefore every transaction affects the accounting equation.
Ti: Mr. Lee Invested cash of P100,000 and land worth P300,000
in the business.
Assets = Liabilities Owner’s Equity
T2: Mr Lee borrowed P100,000 from the bank.
Assets = Liabilities Owner’s Equity
T3: Mr. Lee received P20,000 cash for services rendered to
customer
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
T4 —Mr. Lee paid P5,00C) the salary of his helper.
Assets = Liabilities ÷ Owner’s Equity
http://www.a-systems.net/accounting-terms.htm
http://content.moneyinstructor.com/1413/basic-accounting.html
http://accountingexplained.com/financial/introduction/chart-of-accounts
Martes, Agosto 22, 2017
The Meaning of Life | Work
boredom is death
wealth is comparative, happiness is comparative, so is all emotions, it's just a deviation from the base emotion
why then do people continue to live? I don't know
but I should know the reason why I continue to live
was it
to
eat?
was it to surf again the internet? was it to be my loved ones? was it to play? was it to study?
thinking all about this I live day to day, without direction, without project to work on,
I don't build something
I don't destroy something
Time just pass
was it to be productive? to produce? to refine? to advance? to be better?
but that's infinite! there's no limit to be "better"
What then is the goal, what then is the standard of human perfection?
When everything depends on one's knowledge and understanding
When everything depends on one's intelligence
Find myself
and live in reality
along with my delusion
and what is the truth but one
yet multitudes of perspective
play the dance of the universe and let it guide me
because life just happens
sometimes life is just created
be the perfection
be the standard
be. me.
I am God.
Everything I say will be true,
Every thought that I will hold will bring beauty to the world
I am justice, I bring humility to the proud
I am joy, I bring happiness to the sad heart
I am God.
I am the golden standard of everyone around me.
No pretense.
No fakery.
I am God.
I play, I laugh, I work.
What then I will bring to this earthly kingdom?
I just want to experience it, to become a part of the play that I made, to be alongside my fragments
How do I look, how do I smell, how do I love, what is this, what is that, this is pleasant, this is augh
how did I get here, why am I here, without the demands of reality, I return to my state, God in flesh, everything was made perfect, what then should I do? What then should I do? Help? Volunteer?
Lunes, Agosto 21, 2017
gutenberg
mit.opencourse
scrbd
http://gen.lib.rus.ec/search.php?req=sme+handbook&open=0&res=25&view=simple&phrase=1&column=def
http://accessengineeringlibrary.com/
*saintlu
*pass: engineering
https://www.scribd.com/document/269954642/Solutions-Manual-Engineering-Mechanics
Use Laptop Keyboard as Phone Keyboard
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=de.onyxbits.remotekeyboard&hl=en
Here's how to do it:
Note: Both Laptop and Phone should be online
*On the Phone
1. Install RK
2. Set as default keyboard
I did it by: Settings>Language and Input>Default Keyboard>Remote Keyboard
*On the Laptop
1. download PuTTY
2. Run PuTTY
3.https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/optical-networking/ons-15454-sdh-multiservice-provisioning-platform-mspp/66069-ene-gne-putty.html
In the Beta State
AI have been sleepy, tired, maybe because it's already night, maybe because I just ate fried pork sausage, but I feel sloppy, a brain mud
...then someone just farted
...A deep pause of silence
A burst of laughter!
Then everyone blames everyone
I don't feel shit anymore, its just clean, awake state again
A good laugh do wonders ever time :)
HOW TO ACHIEVE THE BETA STATE
1. Stop all visual motion. That means I will disable all android animations. I will take the front seat in the jeepney and stop side glancing.
I will use firm and concise words.
What are the pros being in the beta state? It will save me in college.
What are the cons?
Red eyes.
2. Fast
I will not eat meat and starch in 12 hours straight for one day.
When?
Three days before full moon and three days before new moon, when the grip of the Moon starts to weaken.
What is this fasting all about?
The fasting is all about Ekadashi fasting. A cosmic event perfect to ground myself with the earth which I will align myself with Schuman's resonance, the sound of Om, the sound of the universe.
That was deep, do I have technical knowledge why are you fasting?
The moon has an affinity for water, especially saline water. Keep in mind that a human body is mostly water every single cell was enveloped in fluid membrane. When the pull of the Moon will have an effect, it will cleanse the impurities of the cells by attracting sodium.
It is important to stay hydrated in this stage to fully optimize the moon's gentle cleansing. Take fruits and juices that are fortified with magnesium and iron, also with zinc and copper, and in the morning take calcium and sodium.
From Bowel's Reaction Series, the Continuous right is the solidification from calcium rich mineral to sodium rich mineral. Specifically, it starts with calcium, then potassium, and finally sodium.
The Discontinuous left is the mafic minerals which are magnesium and iron rich starting from olivine to p.....
Linggo, Agosto 20, 2017
Environmental Engineering | Introduction
- Appropriately putting into practice environmental conservation methods
- Using the right tools to explore resources
- Adding value to our resources
- Making sure machines are maintained appropriately
- Thorough training of human resources
- Provision of effective and efficient supervision
- Using the right techniques to minimize exploitation
- Using sustainable wood products
- Using organic foods
- Embracing the 3R’s, reduce, reuse, and recycle
- Purchasing sustainable seafood
- Supporting conservation campaigns at local levels
- Conserving power
- Minimizing consumption of meat
- Utilizing eco-friendly cleaning products
- Offer suggestions for maintaining and beefing up environmental performance
- Find out, evaluate and apply storm water good management practices for municipal, industrial and construction stormwater programs
- Evaluate environmental regulations and seek counsel with applicability determination
- He or she should document all environmental incidences
- Develop and keep in line environmental management systems to conform to air and permit regulations.
- Lead from the front in the negotiation and of permit applications
- Liaise with regulatory bodies, prepare required documentation, organize any testing sessions and provide more follow-up documentation needed.
Sabado, Agosto 19, 2017
Blogger App on Android
Aptoide--->Blogger/ Merriam-Webster Dictionary Premium/ Twilight Pro
Biyernes, Agosto 18, 2017
Physical Geology 13 | Chapter 2
Which of the following is NOT a type of silicate structure?
Need a Hint?
A) loop silicate
B) double chain silicate
C) single-chain silicate
D) sheet silicate
2
Which of the following are true for a mineral.
Need a Hint?
A) It is inorganic.
B) It is a solid crystalline substance.
C) It is naturally occurring.
D) All of these are properties of a mineral.
3
The silicon-oxygen tetrahedron is:
Need a Hint?
A) the building block of the silicate minerals.
B) composed of 4 oxygen atoms surrounding 1 silicon atom.
C) composed of the two most abundant elements on Earth.
D) all of these
4
The mineral, olivine, is an example of:
Need a Hint?
A) a double-chain silicate structure
B) a sheet silicate structure
C) a framework silicate structure
D) an isolated silicate structure
5
What type of bonding occurs between sodium (Na+2) and chlorine (Cl-2) in the mineral halite?
Need a Hint?
A) covalent
B) weak electrostatic bonds
C) metallic
D) ionic
6
Coal is a rock and not a mineral because:
Need a Hint?
A) it contains only one element: carbon
B) it is made of partially decomposed organic matter
C) it is too soft to be a mineral
D) it does not have cleavage
7
Atoms with either a positive or negative charge are called:
Need a Hint?
A) radioactive
B) elements
C) ions
D) isotopes
8
The type of bonding where electrons in the outer shell of an atom are shared with the adjacent atom:
Need a Hint?
A) ionic
B) weak electrostatic bonds
C) metallic
D) covalent
9
A unit of matter which cannot be broken down into other substances by ordinary chemical methods is:
Need a Hint?
A) an element
B) an atom
C) a molecule
D) a mineral
10
Which of the following is true of a single silica tetrahedron?
Need a Hint?
A) It has a net negative charge.
B) It has one silicon atom and four oxygen atoms.
C) The atoms of the tetrahedron are strongly bonded together.
D) All of these are true of a single silica tetrahedron.
11
The ability of a mineral to break along preferred planes is called:
Need a Hint?
A) brittleness
B) hardness
C) fracture
D) cleavage
12
Which of the following are minerals?
Need a Hint?
A) all of the choices below are minerals.
B) calcite
C) quartz
D) salt
13
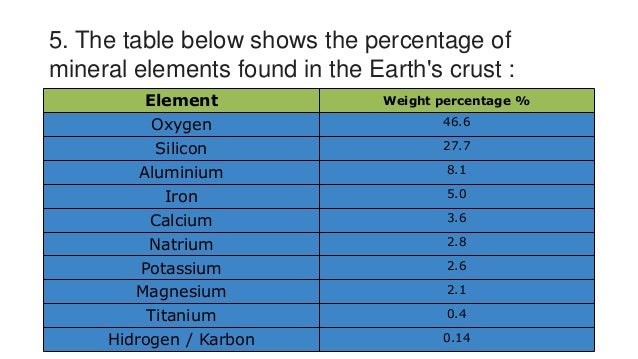
Oxygen accounts for what percent by weight (approximately) of all matter in Earth's crust?
Need a Hint?
A) 12%
B) 24%
C) 36%
D) 47%
14
Amphibole is:
Need a Hint?
A) a sheet silicate
B) a single chain silicate
C) a framework silicate
D) a double chain silicate
15
Protons are sub-atomic particles:
Need a Hint?
A) which orbit around the nucleus of the atom.
B) with a positive electrical charge.
C) with a negative electrical charge.
D) with variable atomic mass.
16
An ion with a surplus of electrons is:
Need a Hint?
A) an isotope.
B) neutral.
C) positively charged.
D) negatively charged.
17
Stable isotopes are elements that:
Need a Hint?
A) have variable numbers of protons.
B) do not lose protons and neutrons over time.
C) are radioactive.
D) none of these.
18
Which of the following mineral pairs are not polymorphs??
Need a Hint?
A) calcite and aragonite
B) diamond and graphite
C) fosterite and fayalite
19
The most common group of minerals are the:
Need a Hint?
A) sulfides
B) silicates
C) oxides
D) carbonates
20
Atoms become ions when they:
Need a Hint?
A) gain or lose mass.
B) gain or lose neutrons.
C) gain or lose protons.
D) gain or lose electrons.
KEY: A = 1.9.12
B = 6.15.17.19
C = 7.18
D = 2.3.4.5.8.10.11.1314.16.20
1
Diamonds are the hardest natural mineral.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
2
Gypsum is the softest naturally occurring substance on Earth.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
3
Diamonds are found only in South Africa.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
4
Minerals are composed of compounds.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
5
All silicate minerals are composed of silicon-oxygen tetrahedra arranged in various ways.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
6
By definition, water is a mineral.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
7
By definition, petroleum is a mineral.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
8
By definition, coal is mineral.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
9
Diamonds are formed by carbon subjected to very high pressure deep inside the Earth.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
10
Atoms may gain or lose neutrons.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
11
Atoms may gain or lose electrons.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
12
Eight elements comprise 98.5% of Earth's crust.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
13
The most abundant element in Earth's crust is carbon.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
14
The most abundant element in Earth's crust is oxygen.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
15
The most abundant element in Earth's crust is hydrogen.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
16
All compounds have a crystalline structure.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
17
Common table salt is known to geologists as the mineral, halite.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
18
Some minerals can be scratched with your fingernail.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
19
All minerals display a physical property known as hardness.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
20
All minerals display a physical property known as fracture.
Need a Hint?
A) TRUE
B) FALSE
KEY: TFFFT FFFTT TTFTF FTTTT